# React
# 基础知识
# 生命周期
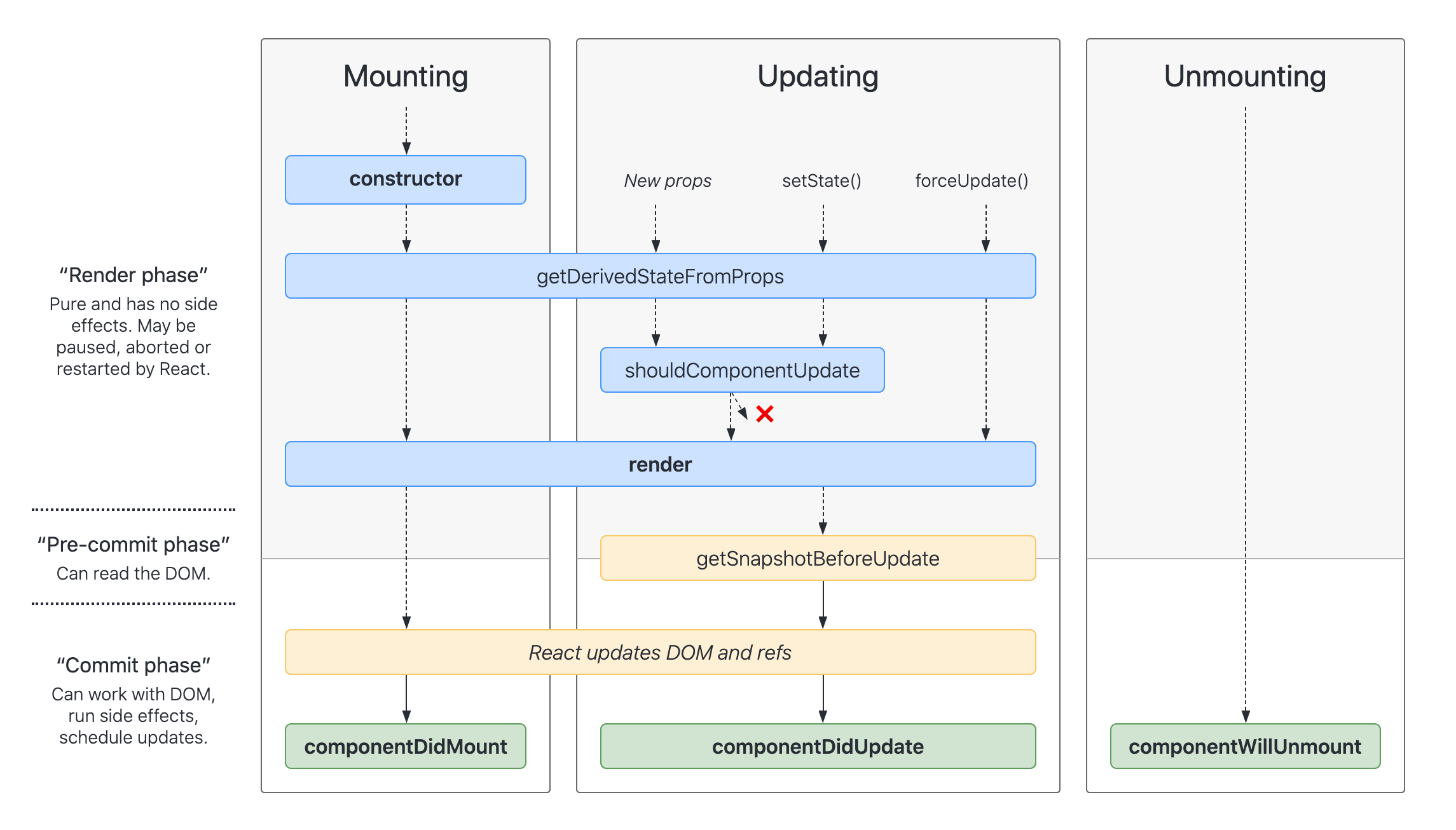
getDerivedStateFromProps 一般只用于表单控件获取默认值,其它情形不推荐使用 (而是用计算属性替代)。
componentDidMount 和 componentDisUpdate 阶段 DOM 已经渲染完成了,这时候可以执行带有副作用的操作。
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 会在 render 之前被调用,用于获取 render 之前的 DOM 状态。它的返回值会被传递给 componentDidUpdate,用于在更新之后修改 DOM。
shouldComponentUpdate 用于性能优化,很多时候可以由 PureComponent 自动实现。
# 受控组件 vs. 非受控组件
对于 DOM 元素来说,加了 value 属性就是受控组件 (opens new window),<input type="text" value={msg} />。不加 value 属性就是非受控组件 (opens new window),这时可以用 Ref (opens new window) 访问非受控组件。
UI 组件库 (而非 DOM 元素),也有受控和非受控的概念。
# 函数式组件 vs. 类组件 vs. Hooks
类组件一直是最经典的写法,函数式组件不能执行副作用,Hooks 的出现让函数式组件能执行副作用。
# Hooks
Hooks 于 React Conf 2018 提出,可以更细粒度地复用代码逻辑,并解决高阶组件 (Higher Order Components, HOC) 的嵌套地狱 (wrapper hell) 问题 (如下图所示)。

Hooks 还可以解决类组件 (Class Components) 带来的巨型组件 (giant components) 问题,如下所示:
class FriendStatus extends React.component {
render() { return ...; }
componentDidMount() {
this.subscribeToStore(this.props.friend.id)
this.fetchFriendStatus(this.props.friend.id)
this.startTimers()
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 我们很难发现这里是否有正确释放资源
this.unsubscribeFromStore(this.props.friend.id)
this.cancelPendingRequests()
this.stopTimers()
}
}
Hooks 的限制:不能在条件语句内使用 if (props.condition) { useState() }
# HOC vs. Hooks
高阶组件 (HOC) 是一个函数,输入一个 Component,返回另一个 Component,能够实现一些代码复用需求,类似装饰器模式。HOC 本身并不是 React 的一部分,只是一种高级的编码技巧。
下面是使用 HOC 的一个例子,思想就是使用函数 wrap 了一层,代码上还是很绕的,初学者需要适应一段时间。
使用 HOC 复用计数器代码
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
function withCounter(WrappedComponent) {
return class extends React.Component {
state = { count: 0 };
handleDecrement = () => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count - 1 });
};
handleIncrement = () => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
};
render() {
const { count } = this.state;
return (
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} count={count} onIncrease={this.handleIncrement} onDecrease={this.handleDecrement} />
);
}
};
};
const App = ({ count, onIncrease, onDecrease }) => {
return (
<div>
<div>Current count: {count}</div>
<div>
<button onClick={onDecrease}>-</button>
<button onClick={onIncrease}>+</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
const AppWithCounter = withCounter(App);
ReactDOM.render(<AppWithCounter />, document.getElementById('root'));
下面是使用 Hooks 的一个例子,比起前面的 HOC 来说,要更加的简洁易懂。
使用 Hooks 复用计数器代码
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
const useCounter = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const onIncrease = () => setCount(count + 1);
const onDecrease = () => setCount(count - 1);
return [ count, onIncrease, onDecrease ];
};
const App = () => {
const [ count, onIncrease, onDecrease ] = useCounter();
return (
<div>
<div>Current count: {count}</div>
<div>
<button onClick={onDecrease}>-</button>
<button onClick={onIncrease}>+</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
# 在 React 中编写样式
三种方式:
- CSS,就是 CSS 原生方式
- CSS Modules
- CSS in JS
CSS in JS 又有很多实现:
- styled-components
- redium
- 等等
# TypeScript
这篇文章 (opens new window)介绍了如何标注 props.children 的类型。
# 状态管理
# Context
# Redux
# 参考资料
- reactjs.org
- medium 上的这篇文章 (opens new window) 提出了 HOC 带来的 wrapper hell 问题,介绍了 Hooks 如何解决这个问题。分别用两种技术实现了一个计数器逻辑复用的例子,并进行比较。
- 《The Road to React》:https://github.com/the-road-to-learn-react/the-road-to-react-chinese
- https://github.com/rwieruch/blog_robinwieruch_content